The Pulse of Aldahai Stables
Explore the latest news and insights from Aldahai Stables.
Magnetic Wonders: A Deep Dive into the Science of Attraction
Unleash the secrets of attraction! Explore the fascinating science behind magnets and their wonders in this captivating deep dive.
Understanding Magnetic Forces: How Attraction Works at the Subatomic Level
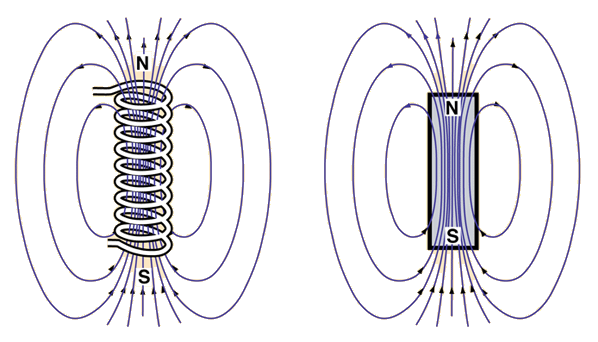
Understanding magnetic forces is essential to grasp how attraction works at the subatomic level. Atoms are composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons, where protons carry a positive charge and electrons carry a negative charge. The fundamental principle of magnetism can be traced back to the electromagnetic force, one of the four fundamental forces of nature. When we delve into the behavior of these particles, we find that moving electrons create magnetic fields. Hence, the phenomena we observe, like a magnet attracting a paperclip, can be attributed to the alignment of atomic structures and their associated magnetic moments.
The interaction between magnetic forces can also be explained through quantum mechanics, which reveals that particles possess intrinsic angular momentum, or spin. This spin leads to the formation of magnetic dipoles, which align themselves in response to external magnetic fields. When similar poles come close, such as north to north or south to south, they repel each other, while opposite poles attract. Understanding these fundamental interactions at the subatomic level not only clarifies the basics of magnetism but also paves the way for technological advancements such as MRI machines, electric motors, and countless other applications that rely on the manipulation of magnetic forces.
Counter-Strike is a highly popular tactical first-person shooter game that has been a staple in the esports community since its initial release. Known for its team-based gameplay, players can choose to be part of either the terrorist or counter-terrorist team, engaging in rounds that emphasize strategy and teamwork. For gamers interested in enhancing their setup, check out the Top 10 magsafe car mounts to keep their devices secure while gaming on the go.
The Role of Magnetic Fields in Everyday Life: Applications and Impacts
Magnetic fields are an often-overlooked aspect of our daily lives, yet they play a crucial role in numerous applications that many people rely on without even realizing it. For instance, magnetic fields are fundamental in the operation of various electronic devices. They are utilized in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machines, which are essential for diagnosing internal conditions in medicine. Furthermore, several household items, such as refrigerators and televisions, depend on magnetic fields to function effectively, highlighting their importance in our modern lifestyle.
The impacts of magnetic fields extend beyond technology and into natural phenomena. The Earth's own magnetic field protects us from harmful solar radiation, a shield that helps maintain life on our planet. Additionally, many animals, including birds and sea turtles, utilize Earth's magnetic field for navigation, demonstrating an innate ability to sense these fields for migratory purposes. Thus, understanding the role of magnetic fields not only enhances our mastery of technology but also deepens our appreciation for the natural world.
What Are the Different Types of Magnetism and How Do They Affect Us?
Magnetism is a fundamental force of nature that affects various materials in different ways. The types of magnetism can be broadly classified into five categories: ferromagnetism, paramagnetism, diamagnetism, antiferromagnetism, and ferrimagnetism. Each type of magnetism arises from the behavior of electrons and their spins within atoms. For instance, ferromagnetic materials, such as iron, can retain their magnetic properties even after an external magnetic field has been removed, making them essential for various applications like magnetic storage devices and electric motors. On the other hand, paramagnetic materials, like aluminum, exhibit only a weak magnetic response and lose their magnetism once the external field is removed.
The implications of these different types of magnetism are significant and far-reaching. They not only play a crucial role in technology but also affect our daily lives in subtle ways. For example, diamagnetism, found in materials like bismuth and graphite, causes these materials to be repelled by magnetic fields, which can lead to innovative applications in levitation technology. Furthermore, understanding the nature of antiferromagnetic materials is essential in the development of advanced spintronic devices that seek to utilize electron spin for faster and more efficient computing. In summary, the study of magnetism not only enhances our understanding of physical science but also drives technological advancements that impact our everyday experiences.